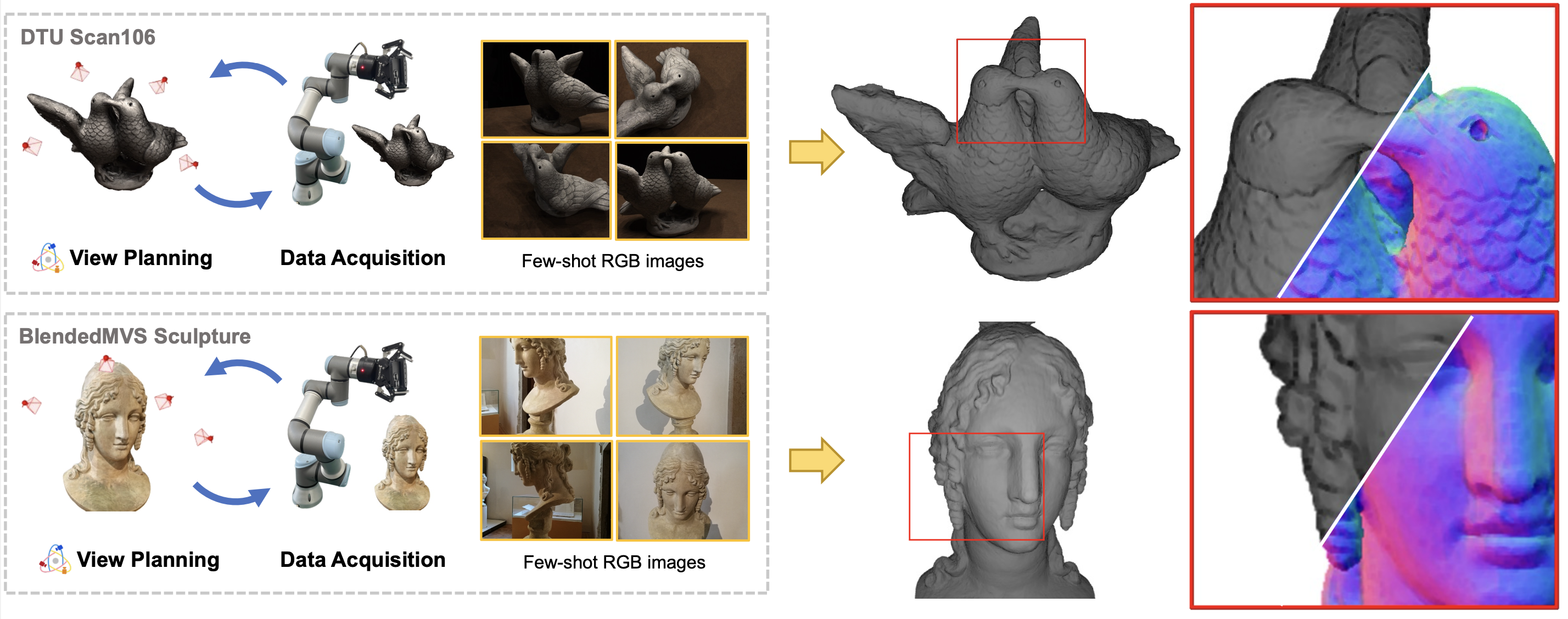
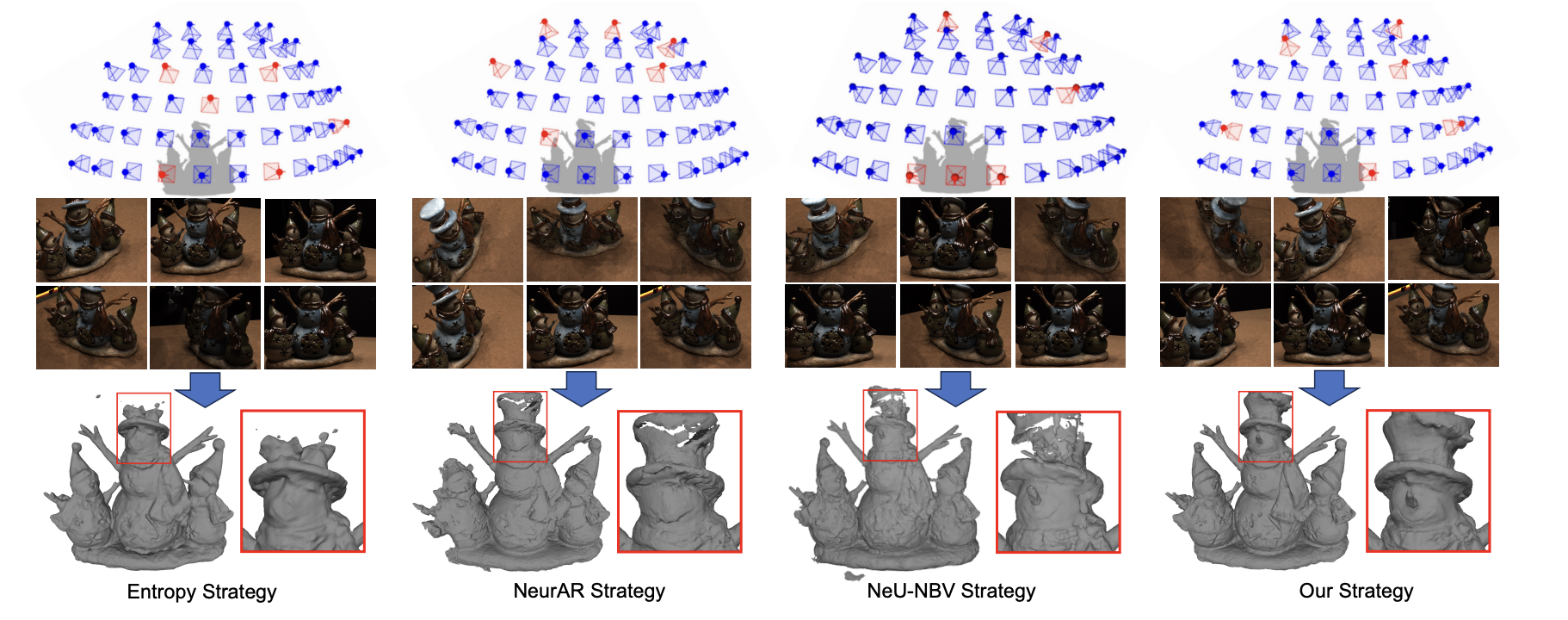
Neural implicit representations have revolutionized dense multi-view surface reconstruction, yet their performance significantly diminishes with sparse input views. A few pioneering works have sought to tackle this challenge by leveraging additional geometric priors or multi-scene generalizability. However, they are still hindered by the imperfect choice of input views, using images under empirically determined viewpoints. We propose PVP-Recon, a novel and effective sparse-view surface reconstruction method that progressively plans the next best views to form an optimal set of sparse viewpoints for image capturing. PVP-Recon starts initial surface reconstruction with as few as 3 views and progressively adds new views which are determined based on a novel warping score that reflects the information gain of each newly added view. This progressive view planning progress is interleaved with a neural SDF-based reconstruction module that utilizes multi-resolution hash features, enhanced by a progressive training scheme and a directional Hessian loss. Quantitative and qualitative experiments on three benchmark datasets show that our system achieves high-quality reconstruction with a constrained input budget and outperforms existing baselines.
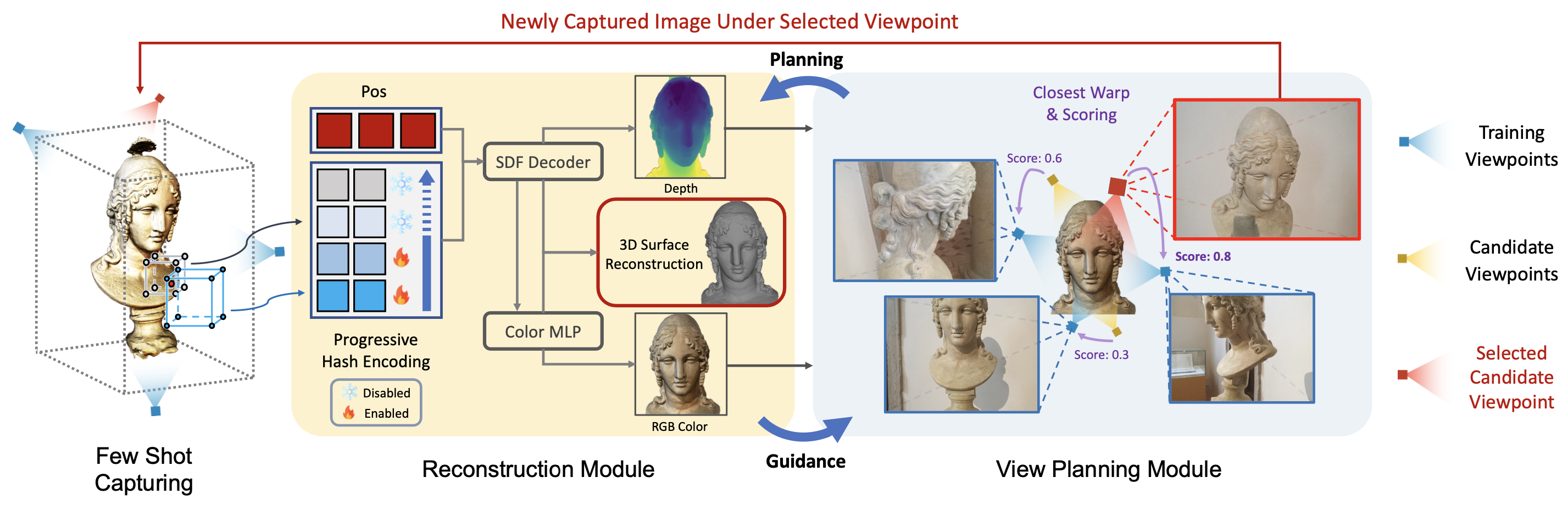
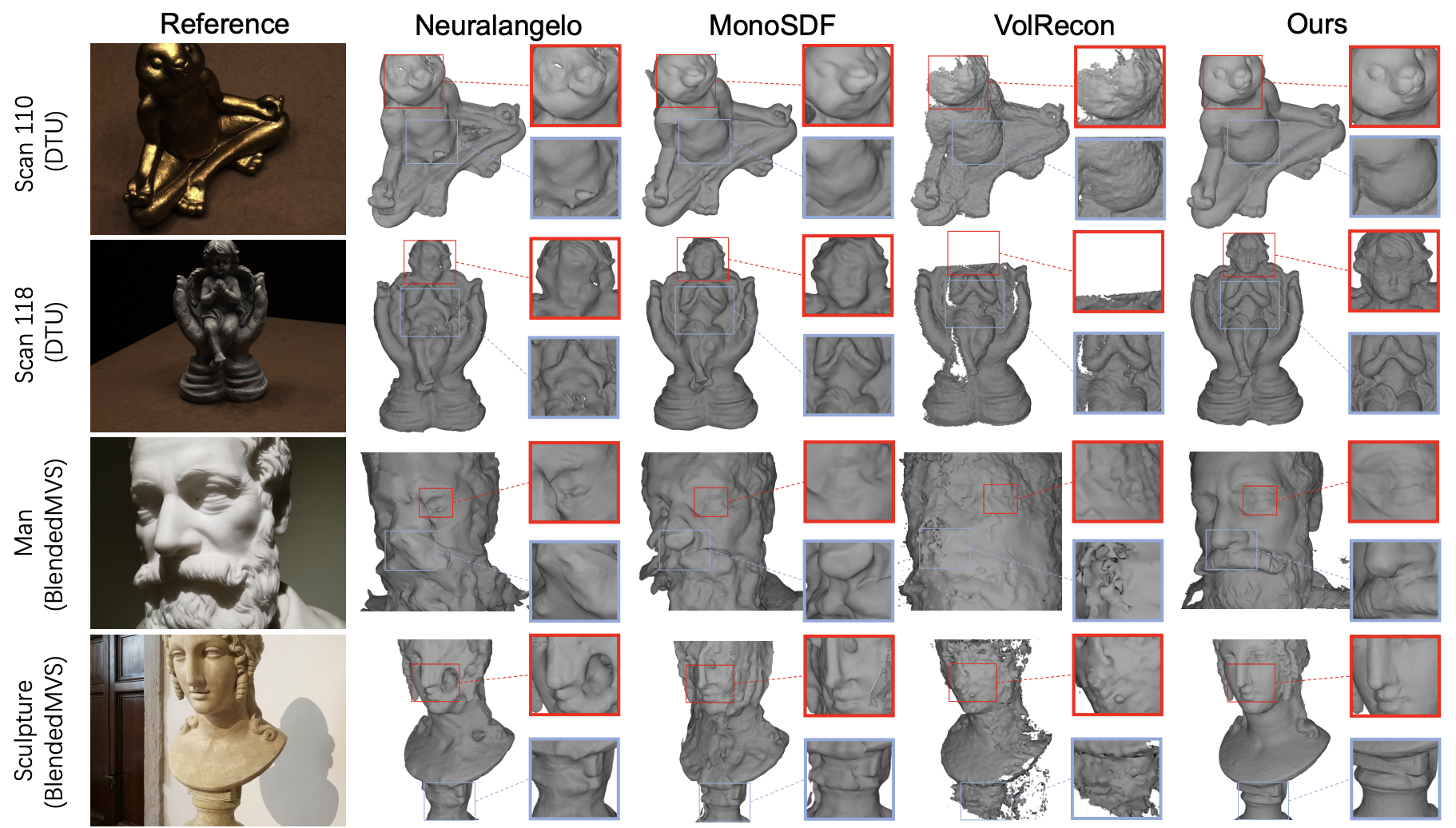
We propose PVP-Recon, a novel system consisting of a view planning module and a reconstruction module, to reconstruct high-quality object surfaces from a sparse set of RGB images. Specifically, the view planning module uses a warping-based strategy to determine the most informative viewpoint for subsequent image capture. The reconstruction module adopts a progressive hash encoding as the geometric representation, facilitated by a novel directional Hessian loss, for reconstructing high-quality object surfaces.
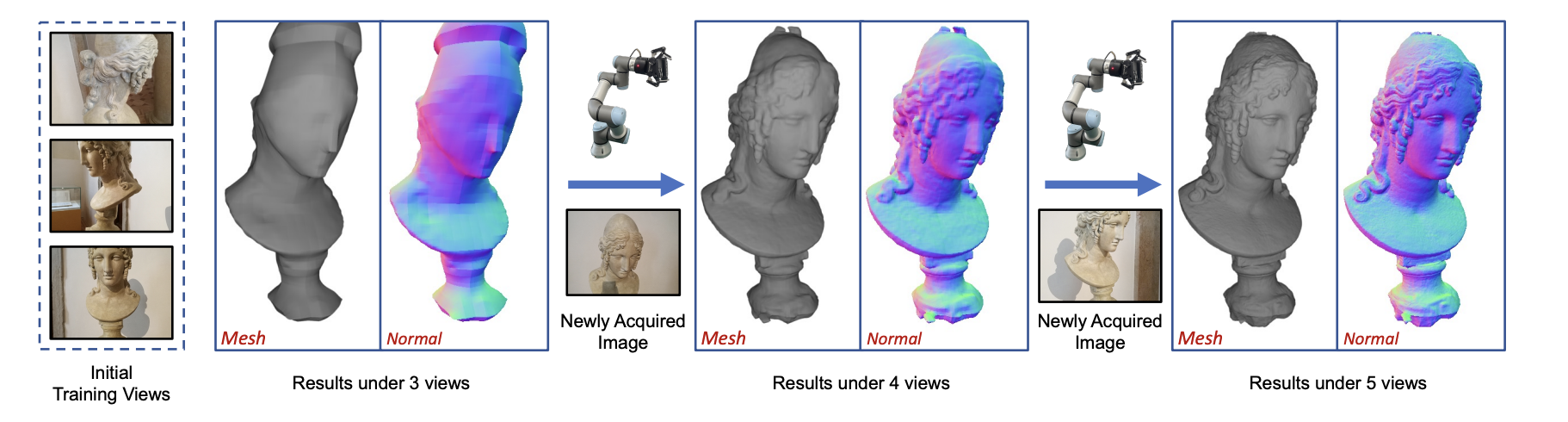
We assume that view planning and surface reconstruction are mutually reinforcing. The newly acquired image from the view planning module is supplemented to the reconstruction module to help its optimization of recovering 3D surfaces. In turn, the reconstruction module provides current optimization status to guide the view planning module to make further planning decisions. We alternately plan subsequent input views and optimize the mesh surface, trying to achieve the best reconstruction results with a few images.

@article{ye2024pvp,
title={PVP-Recon: Progressive View Planning via Warping Consistency for Sparse-View Surface Reconstruction},
author={Ye, Sheng and He, Yuze and Lin, Matthieu and Sheng, Jenny and Fan, Ruoyu and Han, Yiheng and Hu, Yubin and Yi, Ran and Wen, Yu-Hui and Liu, Yong-Jin and others},
journal={ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG)},
volume={43},
number={6},
pages={1--13},
year={2024},
publisher={ACM New York, NY, USA}
}